Microscopic Testicular Sperm Extraction (microTESE) is a surgical procedure used to retrieve sperm from the testicles of men with non-obstructive azoospermia, a condition characterized by an absence of sperm in the ejaculate due to problems with sperm production in the testes. Unlike obstructive azoospermia, where sperm production is normal but the ducts carrying sperm are blocked, non-obstructive azoospermia involves impaired sperm production within the testes.
Pre-operative Evaluation: Before microTESE, men undergo a thorough evaluation by a fertility specialist to determine the cause of azoospermia and to assess whether microTESE is appropriate. This evaluation typically involves a physical examination, hormone tests, genetic testing, and imaging studies such as testicular ultrasound.
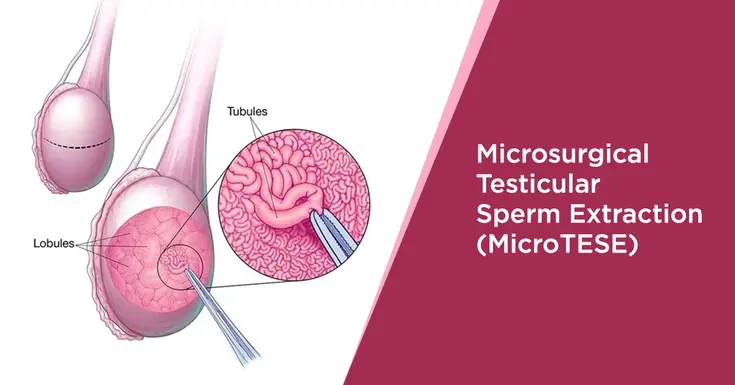
Surgical Procedure: MicroTESE is performed under general anesthesia. During the procedure, a small incision is made in the scrotum, and the testicular tissue is exposed. Unlike traditional TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction), which involves blindly obtaining tissue samples from the testicles, microTESE utilizes an operating microscope to identify areas of the testes where sperm production is most likely to occur.
Microscopic Dissection: With the aid of the microscope, the surgeon carefully examines the seminiferous tubules, the structures within the testes where sperm are produced. Small samples of tissue containing seminiferous tubules are collected selectively from areas that appear to have the highest chance of containing sperm.
Sperm Retrieval: The collected tissue samples are then examined under the microscope in the operating room to search for the presence of sperm. If sperm are found, they are isolated and retrieved from the tissue for use in assisted reproductive techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Post-operative Recovery: Recovery from microTESE is typically quick, with most men able to return home on the same day as the procedure. Mild discomfort and swelling in the scrotal area are common after surgery, but these symptoms generally resolve within a few days. Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities and sexual intercourse for a period of time to allow for proper healing.